The amount of healthcare data generated today is astounding. Over the past ten years, big data in healthcare grew at a record 568%. Smart endoscopes, surgery robots, connected remote patient monitoring systems, EHR, and telehealth platforms — all of these provide healthcare professionals with previously unimaginable access to data and enable more advanced big data analytics scenarios.
What is the Role of Data Analytics in Healthcare?
Data analytics helps medical professionals make better sense of hundreds of informational bits they receive per day. Medical equipment, patient images, nursing notes, and new results of clinical trials — medical professionals require a ton of conclusive evidence for decision-making.
Data analytics in healthcare helps process a vast number of data sources at higher speeds and with improved efficacy. So that professionals could improve the quality of treatment, better predict patient outcomes, personalize care for chronic diseases, and enhance the quality of people’s lives in general.
Over the past several years, healthcare data has become more accessible:
- Over 95% of hospitals in the US adopted Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems.
- Over 60% of hospitals in the US now use IoT devices.
- In the UK, over 90% of people are also willing to share relevant healthcare data with the NHS for any purpose.
Data analytics in the healthcare industry helps transform this raw intel into actionable insights and new knowledge about different diseases, drugs, and treatment methods. Big data analytics, in particular, focuses on operationalizing unstructured data, which now makes up roughly 80% of all generated healthcare data.
Benefits of Data Analytics in Healthcare
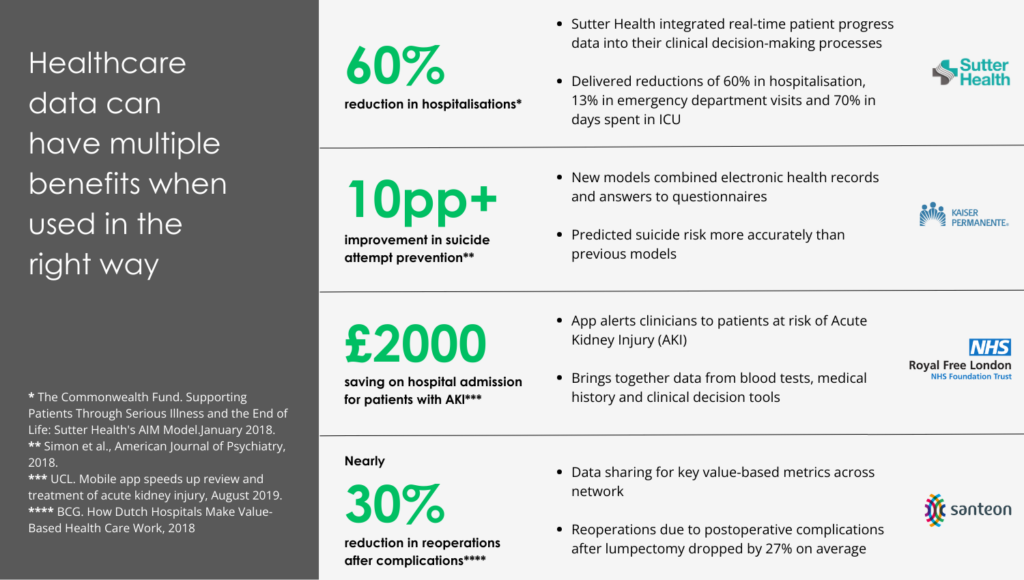
Source: BCG
More data enables more advanced analytics scenarios. Instead of relying purely on observations, medical professionals can back their professional judgment with real-time insights into patients’ vitals, as well as historical data trends.
Fundamentally, the main advantage of big data in healthcare is the new ability to perform exploratory data analysis and advanced data modeling to uncover new patterns, trends, and correlations in ample data reserves.
In practice, the use of data analytics in healthcare enables:
- Better clinical care. With the help of big data analytics, medical professionals can analyze a wider volume and variety of clinical data to measure the patients’ responses to proposed treatment protocols, identify potential healthcare issues at the onset, and suggest preventive or early intervention measures.
- Improved diagnosis. Algorithms can effectively identify anomalies and compare data points with precision few humans can master. Analytics systems can help doctors better compare and evaluate different systems to identify complex or rate diseases correctly, plus detect potential ailments at early stages.
- Advanced preventive care. Using big data, predictive analytics in healthcare can determine the likelihood of developing a certain condition and predict future patient outcomes. With this knowledge, healthcare professionals can suggest preventive measures to avoid expensive hospitalizations, saving the costs for medical institutions, insurance companies, and patients.
- Accelerated clinical research. Advanced analytics systems can facilitate candidate recruitment and evaluation for new clinical studies, bringing a higher degree of objectivity and diversity. Moreover, algorithms can be trained to monitor the progress of clinical trials. For example: Notify staff about adverse events or pinpoint new trends in drug efficacy.
- Personalized treatment. Big data analytics provides medical professionals with a wider range of historical and predictive insights about the patient’s health, which helps with treatment plan personalization. In combination with digital therapeutics (DTx), big data analytics can also help personalize patient care at scale.
6 Viable Use Cases of Big Data and Analytics in Healthcare
Healthcare professionals worldwide use data analytics to transform fragmented, siloed data into new clinical evidence and operational insights. Here are six examples, showing the transformative potential of big data analytics in healthcare.
1. Prediction of Hospital Admissions and Readmissions
Overcrowding is a common problem in hospitals. Many institutions are short-staffed and the irregular patterns of admission further strain operational capacities.
Predictive analysis is one of the main use cases of big data in healthcare. By operationalizing historical data on hospital admissions with statistical modeling techniques, hospitals can learn to better anticipate the demand trends.
For example, the Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris (AP-HP), the largest university hospital in Europe, partnered with Intel to create a cloud-based data analytics system for predicting the expected number of patient visits and hospital admissions. The prototyped system allows AP-HP hospital administrators to review 15-day predictions of emergency department visits and hospital admissions so that they can optimize staffing levels accordingly.
Data from medical devices can also take this analytical approach a notch further, enabling hospital readmission predictions. To determine the likelihood of a specific patient being readmitted you’ll need data parameters such as:
- Patient demographic
- Medical history and comorbidities
- Initial admission details
- Medication and hospitalization history
- Lab results and diagnostics
All of this data is already either available in the EHR systems or can be collected from remote patient monitoring systems and then integrated into a centralized data storage repository, from where it can be queried with analytics models.
Edvantis has recently helped Semdatex — a German provider of patient telemonitoring software — create a secure process for collecting clinical data in real-time from a wide array of wearable, CIED, and other external telemedical devices. With such a system in place, organizations can then deploy custom data science models to run a wide range of predictive scenarios.
2. Early Disease Detection and Prediction
Treating ailments at early stages of development is easier than dealing with progressive cases. Yet, it’s easy to miss many diseases on the onset, especially when patient data appears inconclusive.
Take sepsis: 62% of people discharged with sepsis will be readmitted within a month because of its high persistence and known complications. But treating sepsis is hard because of variability in presentation and the absence of a single definitive test for sepsis. Symptoms often overlap with other conditions, making timely detection hard.
Dignity Health, the largest not-for-profit hospital provider in California, found that big data analytics can predict the likelihood of developing sepsis with high results. The developed system uses natural language processing (NLP) and an analytics engine to continuously scan the electronic medical records of all patients in its facilities for signs of sepsis infection. In high-probability cases, the platform alerts the primary nurse or physician.
In total Dignity Health monitors 120,000 lives per month in 34 hospitals and manages 7,500 patients with potential sepsis per month with the new analytics systems. Since its adoption, sepsis mortality rates in hospitals decreased by 5% on average.
Another great example of data analytics in healthcare comes from researchers from Nottingham University. The team successfully demonstrated how predictive analytics can help prevent heart disease.
The team tasked several algorithms to analyze a dataset of 378,256 patients from some 700 UK GP practices and estimate the likelihood of some patients experiencing cardiovascular events. The top-performing analytical algorithm (a neural network), correctly predicted 7.6% more patients who eventually developed cardiovascular disease compared to the standard risk prediction algorithm.
3. Faster Drug Discovery and Development
Through the use of machine learning algorithms, data analytics is revolutionizing drug discovery and development. By relying on advanced algorithms researchers can identify potential drug candidates with higher efficiency, reducing the time and cost of drug development.
Even the traditionally conservative US Federal Drug Administration (FDA) agrees that:
AI/ML’s growth in data volume and complexity, combined with cutting-edge computing power and methodological advancements, have the potential to transform how stakeholders develop, manufacture, use, and evaluate therapies. Ultimately, AI/ML can help bring safe, effective, and high-quality treatments to patients faster.
In fact, in 2021 over 100 drug and biologic applications submitted to the FDA included mentions of usage of machine learning and advanced analytics.
Advanced analytics models can help weed out poor drug candidates. On average, 90% percent of all drugs fail once they are tested in humans either because they have too many side effects or no effects at all. Machine learning intelligence models can help find the optimal drug candidates faster by analyzing different compound combinations and evaluating different molecules for efficacy and toxicity.
AstraZeneca is one of the companies using data science and ML for drug discovery. It relies on algorithms to identify the best-performing chemical components across 70% of its small molecule chemistry projects. Advanced data analytics also helps this healthcare company develop new therapeutic modalities such as peptide or protein therapeutics, nucleotide-based therapeutics, and cell-based therapeutics.
4. Improved Operational Decisions
Healthcare workforce shortages have been raging for several years now — and hospitals need to do more with fewer people. There are many examples of data analytics in healthcare, aimed at improving tactical decision-making when it comes to triage, admissions, and discharges.
Oftentimes, patients get admitted to the wrong department (e.g., a general ward rather than an ICU) due to limited capacity. Statistically, this results in longer hospital stays and higher readmission rates. Data analytics can be used to predict the anticipated number of admissions, discharges, and transfers to and from the ward, giving healthcare professionals extra knowledge to better handle the bed turnover process.
The Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, in collaboration with the MIT research team, implemented a predictive dashboard to support admission and transfer decisions. It provides real-time information on each ward’s current census as well as the projected number of discharges, allowing the teams to better plan patient rotation. Boston Children’s Hospital uses a similar predictive patient placement system, which informs the emergency department which patients would likely be admitted to the hospital and to which ward.
5. Faster and More Accurate Diagnostics
Medical imaging is vital for delivering accurate diagnosis. Yet analyzing and processing radiology images manually is expensive and requires a lot of human effort. Machine learning algorithms can be effectively trained to analyze images with high precision, identify anomalies, and compare cases across thousands of visuals in the database.
Google Health has some of the most impressive examples of big data analytics in healthcare diagnostics.
By combining computer vision and image search capabilities, Google Health has built an online tool for skin, hair, and nail conditions analysis. DermAssist is a Class 1 Medical Device that is undergoing market testing through a limited release. The app has already shown efficacy in identifying over 80% of the conditions seen in clinics and more than 90% of the most commonly searched conditions.
Another project from the team is Automated Retinal Disease Assessment (ARDA) — an AI-powered tool for diabetic retinopathy detection. The solution was trained on over 100,000 de-identified retinal scans and validated by a team of ophthalmologists. Today, over 3,000 weekly screenings are performed with ARDA in the EU and India.
6. Procurement and Supply Chain Optimization
Medical organizations consume a lot of resources: from energy and water to specialized equipment and medical supplies. A resilient and efficient supply chain is therefore critical. Yet, a lot of current supply chain processes are far from being effective. Over 80% of healthcare professionals perform manual inventory management and 51% say that the number of manual processes in the supply chain leads to significant challenges.
Indeed, poor inventory practices negatively affect patient care and result in higher resource waste and, by proxy, operating costs. Big data analytics has already shown great potential for supply chain optimization across many industries, healthcare included.
For example, Johnson & Johnson created end-to-end visibility into its supply chain by combining 35+ global data sources into a unified data analytics platform. Using that data, the company can optimize its supply chain in a variety of ways, from keeping shelves stocked across retail partners and ensuring medicine is delivered on time and at the right temperature, to managing global category spending and identifying ways to cut costs.
Data analytics can also help hospitals minimize waste and better manage their resources (medicine, blood supplies, donor organs, etc). Novant Health New Hanover Regional Medical Center, for example, uses a data analytics platform to optimize its blood transfusion processes and evaluate opportunities for improvement and the effectiveness of such interventions.
In just one year, New Hanover’s data-informed improvement efforts have increased patient care quality (with 16 adverse events avoided), decreased the number of unnecessary transfusions, and harnessed the hospital over $695K in cost savings.
Final Thoughts
Big data analytics in healthcare is already helping medical professionals test new drugs, diagnose diseases with higher accuracy, minimize hospital readmission rates, and deliver superior care to patients. With the surging availability of medical imagery and biosignal data, even more use cases of big data analytics will soon emerge.
That being said, advanced analytics implementation in healthcare requires new technical expertise, especially in the areas of data collection, processing, and management, as well as data science. Over the past decade, Edvantis has been helping HealthTech companies launch new digital products. We specialize in medical data management, data integrations, and custom healthcare software development among other service lines. Contact us for a personalized consultation.

